What Happens At Inflection Points – Copyright Christine Comaford Assoc 2012
Why do great companies stop growing? Is it a sales or product issue? Does a key market dematerialize? Nope. It’s much simpler than that.
Business leaders come to me because they want growth, which often involves finding and fixing problems. They want their salespeople to sell more, their engineers to innovate faster and with greater ingenuity, theirclient-care people to better service accounts, and on and on.
Hey, who wouldn’t want to solve all these problems? Yet these are not the real problems. They are merely symptoms of underlying structural problems, indications of people getting stuck in their Critter State—in fight, flight, or freeze. And leaders often put their teams exactly there–albeit unintentionally.
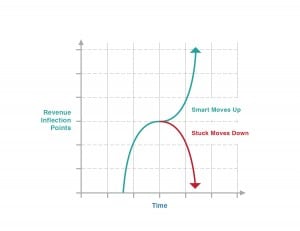
When companies grow, they come to certain places where the things that used to work, the things that created that level of success, don’t work anymore. We call these inflection points. And these crucial points are tied to revenue and company growth.
Here’s the trouble with inflection points: at each one you have a whole new company. At each inflection point, a company must reinvent itself in order to reach it and move through it. If it doesn’t, it will become stuck and ultimately decline into a parabolic upside-down curve, rather than an undulation back into growth mode. (See chart above.)
How do you navigate between inflection points? How do you maintain and increase your momentum to avoid organizational stuck spots—the spots of stasis usually found between inflection points where the company stops growing and swirls around at approximately the same level of annual revenue before sliding precipitously backward? How do you get into the Smart State–the place that will get you to the next inflection point, when the game reaches the next level?
To reach that next inflection point, you will need to intentionally map out a plan to get there, and then execute that plan like a banshee. Either you swirl around the stuck spot, barely maintaining the same revenue year after year, or you slide back down to the previous inflection point, or you move forward with tremendous intentionality. The world is full of “living dead” companies that reached an inflection point and couldn’t grow to the next one. Remember: you’re either moving forward or moving back. Stasis is not sustainable
What Happens At Inflection Points?
To continue to grow, to undulate upwards at an inflection point, a company needs to make changes in each of the following areas: people, money, andmodel.

How To Navigate Key Inflection Points – Copyright Christine Comaford Assoc 2012
People. Some of your team members may need to develop profound new skill sets, behaviors, capabilities, beliefs or identities. Regardless they’ll likely need to become more emotionally engaged and have their lights turned up to shine brighter. As the company passes the higher revenue inflection points, the CEO will need to step back more and more, empowering their executive team to take more responsibility, and in the extreme this can mean a large scale organizational and/or cultural overhaul.
The only way to break the endless cycles of an organizational stuck spot is to start treating the system instead of individual symptoms. But here’s the hitch: Organizations—systems—tend to be reflections of all of the people who work there—especially the leaders. And that means that in order for your organization to change, everyone has to be involved. Starting at the very top of the organization and working all the way down the organizational chart to the people on the front lines. It also means leaders must work on themselves—on their own beliefs and behaviors.
Money. At each inflection point you’ll want to ask a number of money-related questions. How is the business funded? Do you need expansion capital? How are departmental budgets created (or not)? How are costs accounted for and what is the discipline in reporting? Financial systems must be looked into and explicitly altered to fit the next inflection point.
You’ll want to look at how efficient your operations are, how streamlined your expenses are, how you track ROI on all projects—internal and external. Looking at sales will be essential too: does your process of creating and converting new business work well, are your incentive programs motivating, and are sales commissions tied to profit per sale. What are your sales channels? Both your top and bottom lines must be aligned with your growth goal.
To grow to the next inflection point, your systems must be aligned and your funding model must be appropriate. Don’t forget strategic partners, industry influencers, and key alliances, as well as liquidity event planning. Outsourcing or sale of non-performing or low-margin business lines need to be considered here too.
Model. What’s your business model? How will the company grow– organically or via acquisition? As a company grows, core competencies shift, markets (customers, competitors, environment, distribution channels and technology) evolve, and some opportunities are more leverage-able than others. You’ll want to consider whether today’s product line will be the same as tomorrow’s, whether your product path is working and how you can scale your relationships with clients, strategic alliances and key influencers. Oh—and how effective is our marketing?
To grow to the next inflection point, we need a strategic plan. What is yours? Get started by downloading the first 3 chapters from my upcoming book, SmartTribe at www.SmartTribeBook.com.
Christine Comaford is a five-time CEO with 700% ROI on her company exits. She coaches CEOs to achieve remarkable results in performance and operational efficiency by combining neuroscience and business strategy.
Follow her on Twitter (@comaford) and download an excerpt of her upcoming book SmartTribe: Creating a Culture That Outperforms, Outsells, Outinnovates the Competition at www.SmartTribeBook.com.